- Address: Lot No. 20, Zone G, D1 Street, An Ha Industrial Park, Tan Vinh Loc Commune, Ho Chi Minh City
- Phone: (84-28) 668.36156 / 668.36158
- Hotline: 1800.9435
- Fax: (84-28) 3620.4694
- Email: vibo@vibo.com.vn
- Website https://vibo.com.vn/

CHINESE CATERPILLAR FUNGUS AND APPLICATION IN AQUACULTURE FISHERIES
CHINESE CATERPILLAR FUNGUS AND APPLICATION IN AQUACULTURE FISHERIES
- INTRODUCTION
Chinese caterpillar fungus, also known as cordyceps, cordyceps, or cordyceps, is a precious oriental herb that is essentially a parasitic form of the Cordyceps Sinensis fungus (belonging to the Ascomycetes group) on the muscle. Deep body Hepialus Fabricius. The medicinal properties of cordyceps have been shown to be due to the Cordyceps Sinensis mushroom extracts.
The name "Cordyceps Sinensis" is derived from the fact that in summer the Cordyceps Sinensis fungus grows from the worm's head protruding from the ground. In winter they look more like worms (insects), but in summer they look more like a plant (herb).
Particularly the name "Cordyceps" is recorded as the medicine that appeared for the first time in the book "Draft of the outline" in the Ming dynasty by physician Ly Thoi Tran (1575), Cordyceps is ranked as Ginseng in terms of medicinal properties - belongs to the most comprehensive category.
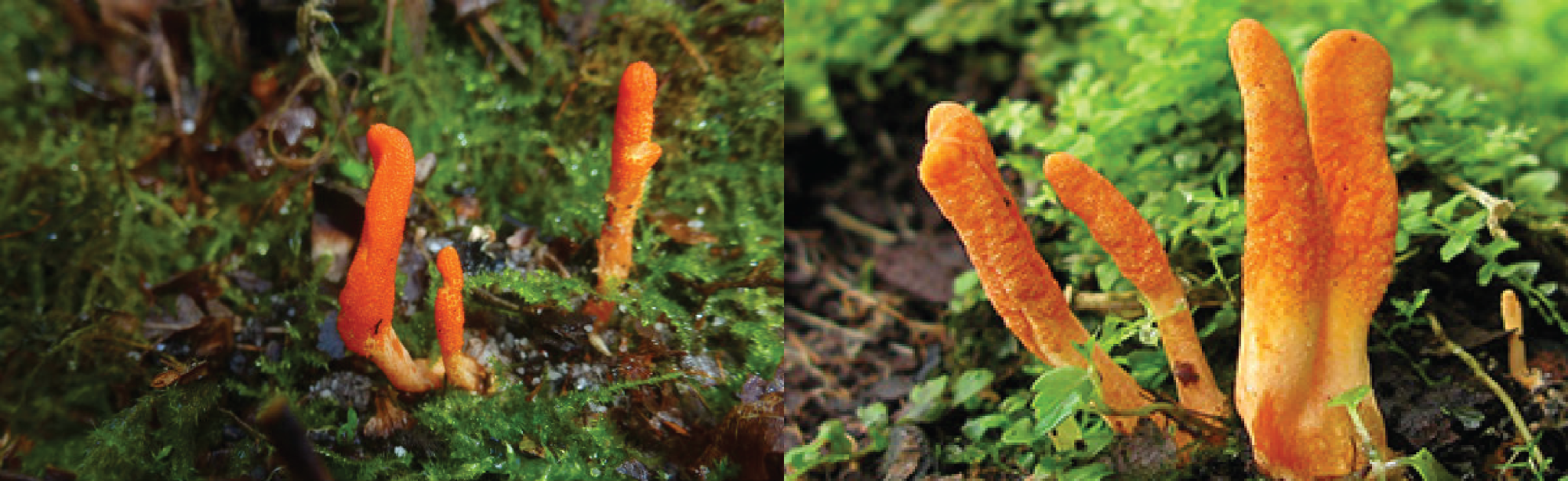

Fig: Cordyceps militaris fruit in the wild
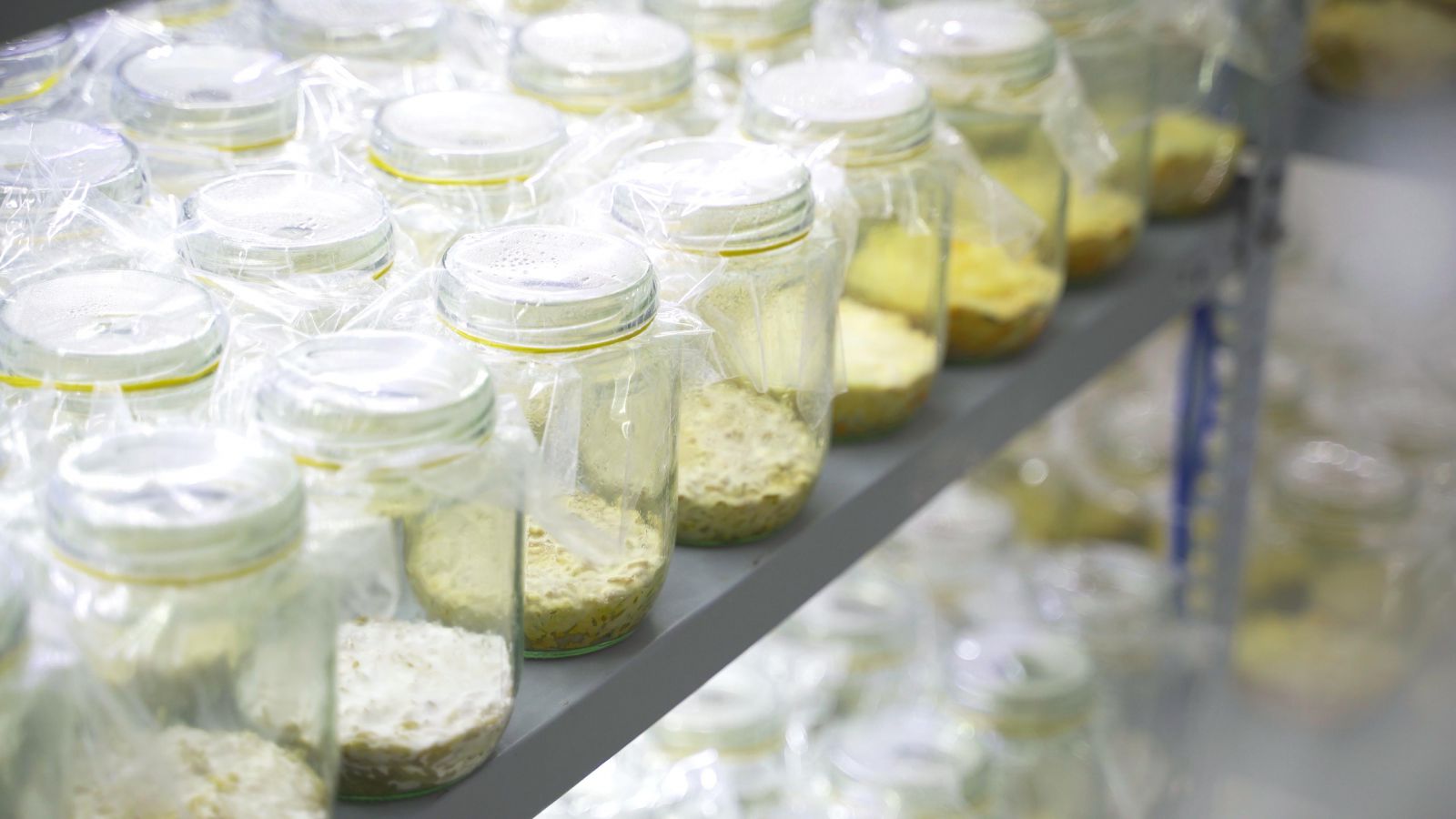 Fig: Cordyceps militaris fruit in artificial culture
Fig: Cordyceps militaris fruit in artificial cultureMore than 400 Cordyceps subspecies have been found and described, however, only about 36 species are cultivated under artificial conditions for fruit fruiting (Wang, 1995; Sung, 1996; Li et al, 2006). Of these species, only C. militaris has been grown on a large scale due to its excellent medicinal properties and a short production period (Li et al, 2006). The fruit of the Cordyceps militaris mushroom is used as food, used in stews, soups, teas ... in Southeast Asian countries such as Hong Kong, Taiwan, China. Safe intake is less than 2.5 g / kg body weight (Che et al, 2003). Fungi fruit and biomass are also used as medicinal and health supplements such as drinking water, capsules, alcohol, vinegar, tea, yogurt, and sauces (Wang et al, 2006). Medicines from these fungi are used to maintain kidney function, lung, anti-aging, sleep regulation, chronic bronchitis. There are more than 30 types of health care products from C. militaris on school competition.
- INGREDIENTS IN COOKING CORN Cordycep militaris.
Chemical analysis shows that in the biomass of cordyceps, there are 17 to 19 different amino acids, with D-mannitol, lipid, and many trace elements (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, Mn, Cu, Zn, Bo, Fe ... in which phosphorus is the highest). More importantly, in cordyceps biomass, there are many bioactive substances that scientists are gradually discovering, thanks to the advancement of the chemistry of natural compounds. Many active ingredients in cordyceps have miraculous medicinal values. Including cordycepin acid, cordycepin, adenosine, hydroxyl-ethyl-adenosine ...
In which, C. militaris mushroom contains many bioactive compounds that have been studied, extracted, and evaluated. Adenosine and Cordycepin are two compounds with high properties and high content of C. militaris fungus. Adenosine accounts for 0.18% in fruiting bodies and 0.06% in fungal biomass. As for cordycepin, the content of the fruit is 3 times higher than that of biomass (0.97% compared to 0.36%) (Hur, 2008).

- SOME PHARMACEUTICAL EFFECTS OF C. militaris
The medical and pharmacological studies have proven C. militaris has many important biological activities such as immunomodulation, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, nervous system, liver, and kidney protection ...
C.militaris has antioxidant activity. High water from different sources of natural C. militaris and cultured Cordyceps mycelium were analyzed for their antioxidant activity using three different test methods, xanthine oxidase test, induction test. hemolysis and lipid peroxide test. The results showed that Cordyceps had strong antioxidant activity in all experiments. CPSI water-soluble polysaccharide, a glucomannogalactan with monosaccharide components of glucose, mannose, and galactose, isolated from C. militaris has shown in vitro antioxidant activity, including hydroxyl free radical capture effect, capacity reducing, and complexing activity with Fe2 +.
Antioxidants play an important role in protecting liver cells from free radical damage. A 2013 study conducted to evaluate the hepatoprotective effects of Cordycepin on an alcoholic mouse liver toxicity model showed that supplementing with Cordycepin in rats' diets was effective in protecting liver cells from harmful effects of alcohol. With the control of silymarin, one of the highly effective substances in liver protection, it can be concluded that Cordycepin has potential in protecting and restoring damage to liver cells [1]. In addition, many studies show that C. militaris effectively increases liver function. It helps strengthen organic cells, immunity, improve liver function and inhibit cirrhosis. C. militaris has the ability to significantly reduce cirrhosis and promote the degradation of collagen. C. militaris polysaccharide acts on liver fibrosis and inhibits astrocytic activation and TGF-β1 expression.
C. militaris extract and isolated ingredients can inhibit and enhance various aspects of the immune system, known as immunomodulation. Immunomodulatory ability enables effective treatment and prevention of diseases caused by immunodeficiency. The activity of compounds isolated from Cordyceps is effective in immunomodulatory action, which includes mitogenicity and activation of immune cells, such as lymphocyte proliferation reactions, and natural killer cell activation. , phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulates IL-2 and TNF-α production ... The therapeutic effect of Cordyceps, such as suppression of immune and allergic diseases, is associated with immunomodulatory effects. One study found that various constituents of polysaccharide from Cordyceps enhanced immune response, spleen index, thymus gland, the phagocytic function of phagocytic cells.
Cordymin, a purified peptide from C. militaris that was found to have anti-cytokines activity in reducing the severity of inflammatory reactions. Cordymin-2 and cordymin-4 showed 53% and 73% inhibitory powers, respectively. Liu et al. (2011) demonstrated the neuroprotective ability of C. militaris mycelium inhibited through an anti-inflammatory model in rats. The chloroform and n-butanol fractions of methanol extract from C. militaris were investigated for anti-inflammatory activity. The extraction test showed that the inhibitory dose was dependent on increased production of inflammatory mediators such as a nitric oxide (NO) through a decrease in the expression of NO synthesis induction.
Clinical studies have shown Cordyceps has the ability to increase bioenergy ATP synthesis. Increasing the synthesis of ATP in cells helps with the rational use of energy and improves the endogenous balance mechanism, thus making the use of oxygen more efficiently. , D-mannitol, polysaccharides, vitamins, and trace elements may be the cause of such an effect. These properties enhance fitness, increase stamina, and fight fatigue.

**References:
Cha, J.Y., et al., Protective effect of cordycepin-enriched Cordyceps militaris on alcoholic hepatotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol, 2013. 60: p. 52-7.